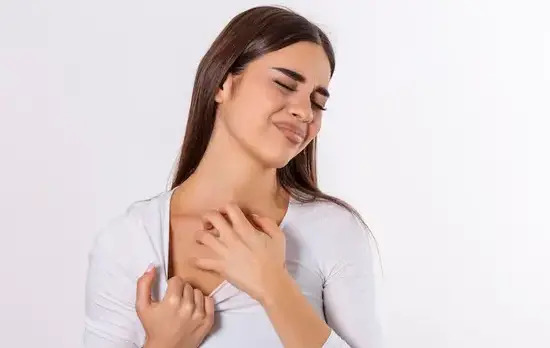
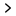Atopic dermatitis can be defined as a red, itchy rash that appears on the skin as a result of the skin’s inability to retain moisture. Reactions can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergens, chemicals, and environmental factors such as temperature.
This skin condition is not contagious, but it is thought to be somehow hereditary and affects approximately 20% of the world’s population.
The main symptom associated with atopic dermatitis is severe and persistent itching. The rashes that appear as a result of the itching tend to be dry and red but has the chance of getting infected and will take longer to heal if a person itches too much.
Treatments can include at-home remedies, over-the-counter medications, and certain medications that have been prescribed by a doctor.
The easiest thing a person can do to help treat his or her atopic dermatitis is to avoid substances and allergens that could irritate the skin more. Proper moisturizing can also help alleviate the symptoms of this skin condition. It is important to remember to use a rich, but unscented, moisturizer which you can apply while your skin is still slightly damp.
Scented cleansers or moisturizers may also irritate the skin and it is advised that a person with atopic dermatitis should choose products that are meant for sensitive skin.
Topical ointments and creams are also available if at-home treatments are not working. These topical treatments usually contain the steroid hydrocortisone, which will help to alleviate the itching and irritation that occurs with atopic dermatitis.
If you decide that over-the-counter medications are still not working on your case of atopic dermatitis, then you should go to a doctor who will be able to prescribe a stronger treatment for you.
A majority of the time, these prescribed treatments are also topical ointments or creams, but they just have a stronger steroids such as corticosteroids.
Featured Image: Freepik @ stefamerpik