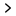Atopic dermatitis, often referred to as eczema, is a type of skin inflammation disease. It is a long-lasting disease, which can cause the skin to be itchy, red, swollen, or cracked. It is usually found in children, but it can occur at any age. Although atopic dermatitis can not be cured, it can be treated by relieving the symptoms such as itching and dryness. Good skincare can also relieve the discomfort and prevent new outbreaks. So it is important to learn more about atopic dermatitis for taking better care of the skin.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
There are some typical symptoms of atopic dermatitis such as itchiness, redness, and dryness. Children under 5 years old may have red, scaly skin on cheeks, front arms, and legs. Itchy, red rashes can usually be found on the neck, knees, and elbows for both infants and adults. Rashes, small bumps, and flakiness can also be found on the face, forearms, and wrists. If it becomes serious, the rashes can bubble up and weep fluid. The skin will be cracked, which hurts and sometimes bleeds. Thus your skin can turn dark, thick, and scarred.
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
There are several causes of atopic dermatitis, but genes are the main cause. This means that a person is more likely to get atopic dermatitis if their family members have ever had atopic dermatitis. Many people with severe eczema will later develop asthma, food allergies, or hay fever over a period of years. It has been found that a lack of certain proteins can cause atopic dermatitis because proteins are important for a normal skin barrier. Irritants, bacterial toxins, and allergens can penetrate the abnormal skin barrier easily. Also, the age of the mother at the time of birth can be another reason. We don’t know why, but infants born to older mother are more likely to have atopic dermatitis than infants born to younger mothers. Last but not least, the environment can also be one of the big reasons for atopic dermatitis. For example, people who live in urban areas with higher levels of pollution or in colder climates are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis.
Treatments of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis cannot be cured. However, there are some treatments that can be carried out to alleviate symptoms and prevent further flare-ups. People with atopic dermatitis can use medications such as antihistamines to reduce itchiness and rashes. They can also use antibiotics to treat bacterial skin infections. Emollients or moisturizers can be applied to keep the skin hydrated and reduce itchiness and cracks. Steroid creams and ointments can also be applied to the skin for reducing redness and soreness. If the inflammation is serious, topical calcineurin inhibitors and ultraviolet light can help to fight the inflammation.
There are also some useful tips to prevent atopic dermatitis flare-ups further. Try to avoid some irritants such as soaps and detergents, allergies like food, wool, and synthetic fabrics, as well as cold and dry weather. Non-cosmetic moisturizers can be applied after showers in order to keep the skin hydrated.
Featured image: DepositPhotos – belchonock